Search Knowledge Base Articles
What are digital wallets?
Digital wallets for cryptocurrency
Most of us carry a wallet. Along with mobile phones and house keys, the wallet is probably one of our most valuable possessions - so now that money has gone digital, it’s no surprise that wallets have followed suit.
What is a digital wallet?
Unlike a traditional wallet, digital wallets don’t store physical currency. A digital wallet is smart as it is a software program – not a pocket-sized flat folding case - which means that a digital wallet can track balances of, as well as send and receive, cryptocurrency.
To keep your digital wallet secure and functionable, you need both a private key and a public key.
In simple terms, the private key is the unique number that lets you access your wallet and initiate transactions on the network. Your public key, as the name suggests, is the number you share with others so that they can view your wallet and send you funds.
Public and private keys are actually a bit more complicated than that, but we’ll cover them in greater detail in an upcoming lesson.
It comes as no surprise that owning a digital wallet is crucial in the world of digital money.
How do you create a digital wallet?
It’s not too difficult to create a digital wallet – in fact, many cryptocurrency exchanges offer customers digital wallets hosted through their exchange.
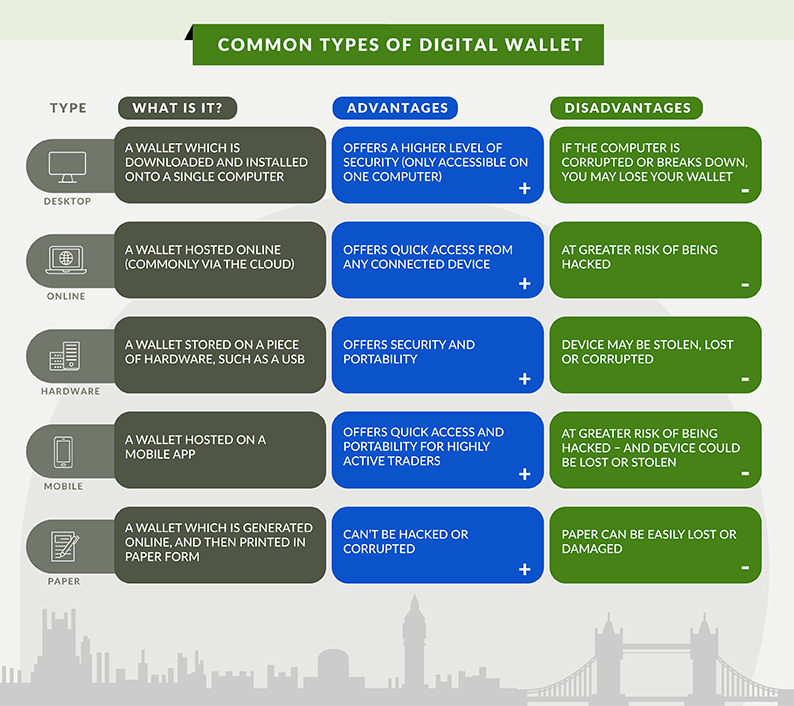
The hardest part of obtaining a wallet is choosing the type of wallet that best suits your needs. Digital wallets come in various forms:
A desktop wallet is downloaded and installed onto a single computer. It is only available on that specific PC or laptop, which offers a high level of security. Of course, if the computer is hacked or gets a virus, you may lose all your digital funds.
Web wallets are hosted online, which in theory makes them accessible from any connected device in any location. A digital wallet that is connected to the internet is known as a ‘hot’ wallet. Online wallets are very easy to access, which is great for very active traders, but since they can store private keys online, they may be more vulnerable to hacking. Thankfully, some web-based wallet providers do offer additional security measures, such as passphrases and two-factor authentication.
A mobile wallet can also be useful. It’s run on an app on your phone and can be used anywhere.
Then there are hardware wallets. The main advantage of a hardware wallet over other wallet types is that your private keys are stored on an offline device like a USB, which increases security.
When it’s time to initiate a transaction, all you do is plug your USB into a connected device, enter the required details and confirm the transaction. These offline or hardware wallets are commonly referred to as ‘cold’ wallets, or ‘cold storage’. We will explore the importance of cold storage in more depth in a later lesson.
A paper wallet is another form of an offline wallet. You can generate a paper wallet with your private and public key, then print it out and store it somewhere safe.
What can you keep in a digital wallet?
You can record all your various cryptocurrency transactions in your digital wallet. The information is stored logically so that you can keep track of what’s coming in and what’s going out – kind of like an online bank account.
How do you access the funds contained within a digital wallet?
Your digital wallet is protected by cryptographic keys known as private keys or master keys. These take the form of hexadecimal codes, which are long and unique numbers.
You cannot access your wallet or authorise transactions without this private key, so it needs to be kept very safe!
Did you find this article useful?
Related Articles
-
What is ioBanker?
ioBanker is introducing the most reliable digital reserves banking features inherited from the ancient concept of “full reserve banking” t...
-
What is digital currency or virtual currency (Cryptocurrency)?
A Digital Currency or Cryptocurrency is a currency in which encryption techniques are used to regulate the generation of units of currency and ve...
-
What countries does ioBanker currently operate in?
As technological and fintech services provider, we do operate worldwide and accept customers worldwide, yet financial services provided through 3rd pa...
-
I can’t find the answer I’m looking for, how do I receive the help I require?
If you were not able to find the help you were after, please email us at: support@iobanker.com and your inquiry will be answered within 48 hours....