Search Knowledge Base Articles
Litecoin explained
Litecoin is a decentralised cryptocurrency created in 2011 by ex-Google employee Charlie Lee. At this point, you could certainly be forgiven for thinking “oh, another decentralised cryptocurrency, whoop-dee-doo”, but it’s definitely worth paying attention to this one!
Why, you ask? Simply because Litecoin, like many other cryptocurrencies, is unique. With over a half-decade on the market, some people would suggest it has the pedigree to serve as a direct alternative to Bitcoin – and perhaps, in time, as a superior option.
What is Litecoin? What’s different about it?
As one of the first cryptocurrencies created in the wake of Bitcoin’s 2009 launch, Litecoin was created as a response to several of the preceding currency’s perceived issues.
In fact, it originally served as a modification of the core Bitcoin protocol.
So, what problems did it solve?
Well, if Bitcoin takes ten minutes to generate a block, Litecoin can do it in two and a half minutes. This allows for much quicker transaction confirmation.
Furthermore, where Bitcoin rewards for mining are halved every 210,000 blocks, Litecoin rewards are only halved after every 840,000 blocks.
Finally, total supply is much, much higher. Where the maximum number of Bitcoins sits at 21 million, the maximum number of Litecoins is 84 million – that’s four times as much (although not unlimited like Ether).
The result? A cryptocurrency that can generate more blocks in less time – and handle a higher volume of transactions – than the Bitcoin network.
SegWit
Like Bitcoin, Litecoin has adopted a ‘soft fork’ known as “Segregated Witness” or “SegWit”.
A soft fork? What’s that?
A ‘soft fork’ is a change to the software protocol which facilitates backwards compatibility, allowing old applications to follow new rules. It creates a temporary split in the blockchain that occurs only when new rules are implemented.
SegWit serves as a means of removing signature data from transactions. This removal of data frees up space and allows a greater number of transactions to be added to the chain. In short, SegWit allows for more transactions to take place, in a faster and more efficient manner.
This might sound confusing at the moment, but don’t worry! There’ll be more on SegWit and ‘soft forks’ in a later lesson.
Litecoin today – and tomorrow
Litecoin was created with the aim of being a better version of Bitcoin. Whether it’s achieved this goal from a technological perspective is up for debate.
Commercially speaking, while it’s among the top five cryptocurrencies in terms of market share, it’s not quite there yet - but it is growing steadily. Cryptocurrency has had an unpredictable history and Litecoin may have an unpredictable future.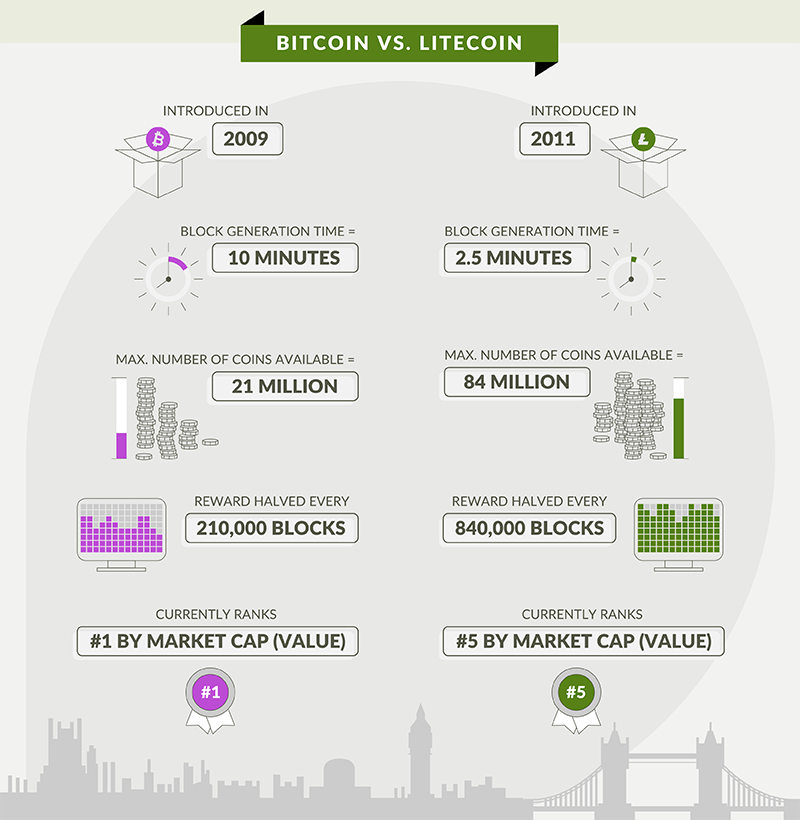
Did you find this article useful?
Related Articles
-
Digital Currency Terminologies
ACH - ACH payments are electronic payments made from one bank to another through the Automated Clearing House network. Many people already use ACH pay...
-
Cryptocurrency explained
A cryptocurrency is a form of digital money. While a traditional currency is recognised by the law of the country that issues it - this is known as le...
-
Blockchain explained
Cryptocurrencies are getting a lot of attention, but there’s just as much buzz around blockchain. There’s a very good reason for this -...
-
Bitcoin explained
Bitcoin, the world’s first cryptocurrency, is something of a trailblazer. Some would argue that Bitcoin has the potential to completely change t...
-
Ethereum explained
Ethereum isn’t a cryptocurrency – it’s the name of the network that is powered by Ether (ETH), which is itself the world’s sec...